Description
Buy Myrin Tablet at Rose Pharmacy Medicine Delivery
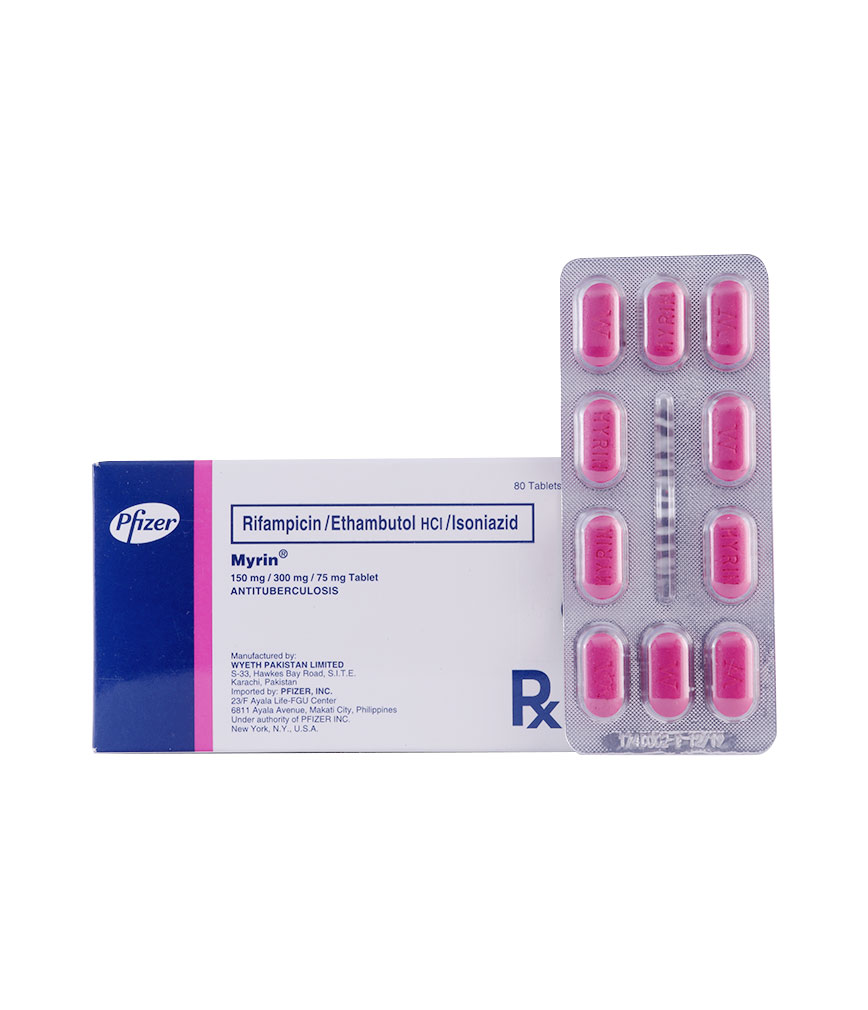
Description :
Each tablet contains ethambutol HCl 300 mg, rifampicin 150 mg, isoniazid 75 mg.
Indications / Uses :
Indicated in the initial and continuation phase of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis. During initial phase which usually lasts 3 months, Myrin is usually administered on a daily continuous basis. When indicated, other antituberculosis drug eg, pyrazinamide, streptomycin may be added. Following the intensive phase, treatment should be continued with Myrin to complete 6 months.
Administration :
Should be taken on an empty stomach: Take 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. If GI irritation occurs, may be taken w/ food or antacids (except Al-containing antacids).
Contraindications :
Patients with a known hypersensitivity to ethambutol, isoniazid or rifampicin or to any of the excipients of Myrin. It is also contraindicated in the presence of alcoholism, optic neuritis, impaired hepatic function and severe renal insufficiency, hyperuricemia and/or gouty arthritis, in the presence of jaundice, or in patients with known retrobulbar neuritis unless the physician determines that it may be used. Patients who are unable to appreciate and report visual side effects or changes in vision (eg, young children and patients with mental illness or mental deficiency).
Special Precautions :
Patients at risk for peripheral neuropathy as a result of malnutrition, chronic alcohol dependence, or diabetes should additionally receive pyridoxine, 10 mg daily. Where the standard of health in the community is low, this should be offered routinely.
Myrin should be administered with care to epileptic patients, since it may induce convulsions, or to patients in psychotic states characterized by mania or hypomania.
Myrin should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus, as management may be more difficult. Patients with decreased renal function need the dosage reduced as determined by serum levels of ethambutol hydrochloride, since the main path of excretion of this drug is by the kidneys.
As with any potent drug, baseline and periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic and hematopoietic, should be performed.
Effects on the Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery: Myrin may diminish visual acuity and colour vision, which may affect the ability to drive and use machines.
Use in pregnancy & lactation: The components of Myrin have harmful pharmacological effects on pregnancy and the fetus. There are no adequate data from the use of rifampicin, ethambutol and isoniazid in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. The potential risk for humans is unknown.
Rifampicin has been shown to be teratogenic in animals on very high doses. When administered during the last few weeks of pregnancy, rifampicin can cause postnatal hemorrhages in the mother and infant for which treatment with vitamin K may be indicated. Because rifampicin has been reported to cross the placental barrier and appear in cord blood, neonates of rifampicin-treated mothers should be carefully observed for any evidence of adverse effects.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. There are reports of ophthalmic abnormalities occurring in infants born to women on antituberculous therapy that included ethambutol hydrochloride. Ethambutol hydrochloride should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Ethambutol hydrochloride has been shown to be teratogenic in pregnant mice and rabbits when given in high doses. When pregnant mice or rabbits were treated with high doses of ethambutol hydrochloride, fetal mortality was slightly but not significantly (p>0.05) increased. Female rats treated with ethambutol hydrochloride displayed slight but insignificant (p>0.05) decreases in fertility and litter size.
In fetuses born of mice treated with high doses of ethambutol hydrochloride during pregnancy, a low incidence of cleft palate, exencephaly and abnormality of the vertebral column were observed. Minor abnormalities of the cervical vertebra were seen in the newborn of rats treated with high doses of ethambutol hydrochloride during pregnancy. Rabbits receiving high doses of ethambutol hydrochloride during pregnancy gave birth to 2 fetuses with monophthalmia, one with a shortened right forearm accompanied by bilateral wrist-joint contracture, and one with hare lip and cleft palate.
Ethambutol is excreted into breast milk. The use of ethambutol should be considered only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the infant.
Isoniazid has been reported to be embryocidal in pregnant rats and rabbits.
Rifampicin and isoniazid are excreted in breast milk. Therefore, infants should not be breastfed by patients receiving Myrin.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.