Description
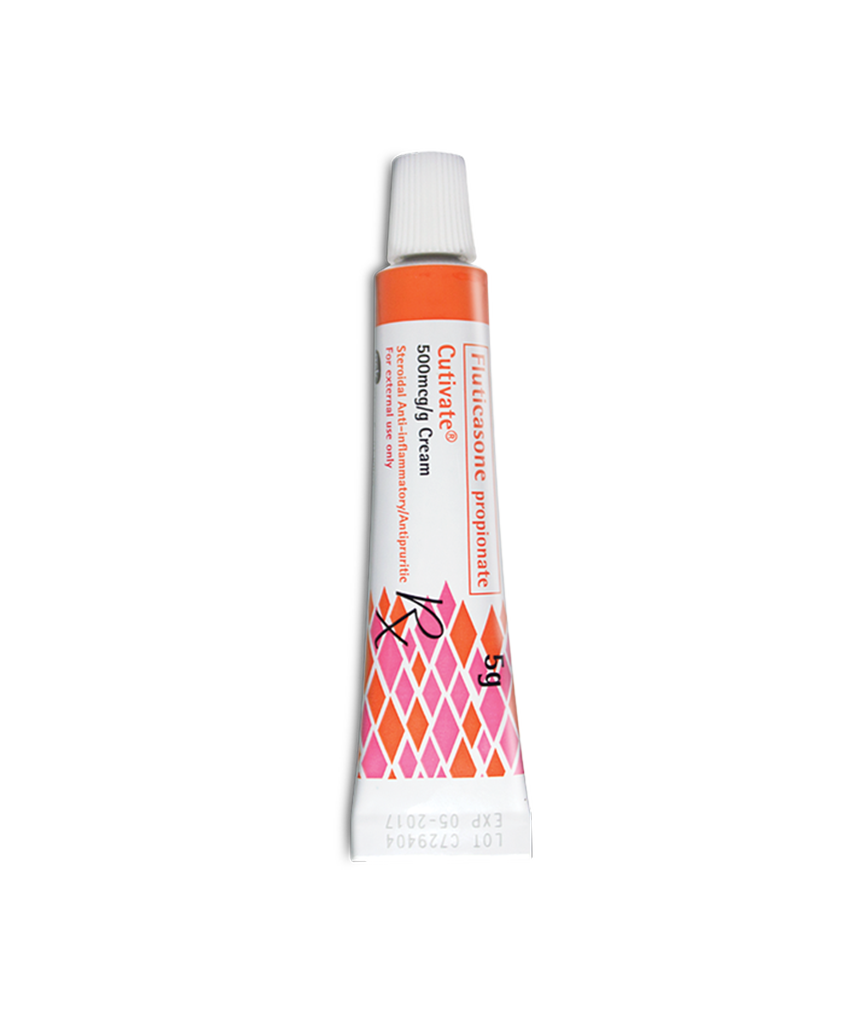
CUTIVATE 0.05% CREAM 5GM
Description :
Each gram of Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream contains 500 micrograms of fluticasone propionate (micronised).
Indications / Uses :
Treatment of Inflammatory Dermatoses: Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream is a potent topical corticosteroid indicated for adults, children and infants aged 3 months and over for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
These include the following: Atopic dermatitis (including infantile atopic dermatitis); nummular dermatitis (discoid eczemas); prurigo nodularis; psoriasis (excluding widespread plaque psoriasis); lichen simplex chronicus (neurodermatitis) and lichen planus; seborrhoeic dermatitis; irritant or allergic contact dermatitis; discoid lupus erythematosus; an adjunct to systemic steroid therapy in generalised erythroderma; insect bite reactions; miliaria (prickly heat).
Reduction of Risk of Release: Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream is indicated for the reduction of the risk of relapse of chronic recurrent atopic dermatitis once an acute episode has been treated effectively.
Contraindications :
The following conditions should not be treated with Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream: Untreated cutaneous infections; rosacea; acne vulgaris; perioral dermatitis; perianal and genital pruritus; pruritus without inflammation; dermatoses in infants under 3 months of age, including dermatitis and nappy rash.
Special Precautions :
Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream should be used with caution in patients with a history of local hypersensitivity to corticosteroids or to any of the excipients in the preparation. Local hypersensitivity reactions (see Adverse Reactions) may resemble symptoms of the condition under treatment.
Manifestations of hypercortisolism (Cushing’s Syndrome) and reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, leading to a glucocorticosteroid insufficiency, can occur in some individuals as a result of increased systemic absorption of topical steroids. If either of the above are observed, withdraw the drug gradually by reducing the frequency of application, or by substituting a less potent corticosteroid. Abrupt withdrawal of treatment may result in glucocorticosteroid insufficiency (see Adverse Reactions).
Risk factors for increased systemic effects are: Potency and formulation of topical steroid; duration of exposure; application to a large surface area; use on occluded areas of skin e.g. on intertriginous areas or under occlusive dressings (in infants the nappy may act as an occlusive dressing); increasing hydration of the stratum corneum; use on thin skin areas such as the face; use on broken skin or other conditions where the skin barrier may be impaired.
In comparison with adults, children and infants may absorb proportionally larger amounts of topical corticosteroids and thus be more susceptible to systemic adverse effects. This is because children have an immature skin barrier and a greater surface area to body weight ratio compared with adults.
Use in Psoriasis: Topical steroids should be used with caution in psoriasis as rebound relapses, development of tolerance, risk of generalised pustular psoriasis and development of local or systemic toxicity due to impaired barrier function of the skin have been reported in some cases. If used in psoriasis, careful patient supervision is important.
Application to the Face: Prolonged application to the face is undesirable as this area is more susceptible to atrophic changes.
Concomitant Infection: Appropriate antimicrobial therapy should be used whenever treating inflammatory lesions which have become infected. Any spread of infection requires withdrawal of topical corticosteroid therapy and administration of appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Infection Risk with Occlusion: Bacterial infection is encouraged by the warm, moist conditions within skin folds or caused by occlusive dressings. When using occlusive dressings, the skin should be cleansed before a fresh dressing is applied.
Chronic Leg Ulcers: Topical corticosteroids are sometimes used to treat the dermatitis around chronic leg ulcers. However, this use may be associated with a higher occurrence of local hypersensitivity reactions and an increased risk of local infection.
Overt suppression of the HPA-axis (morning plasma cortisol less than 5 micrograms/dL) is very unlikely to result from therapeutic use of Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream unless treating more than 50% of an adult’s body surface and applying more than 20 g per day.
Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream contains the excipient imidurea which releases traces of formaldehyde as a breakdown product.
Formaldehyde may cause allergic sensitisation or irritation upon contact with the skin.
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: There have been no studies to investigate the effect of Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) on driving performance or the ability to operate machinery. A detrimental effect on such activities would not be anticipated from the adverse reaction profile of topical Fluticasone propionate (Cutivate) Cream.
Use in Children: In infants and children under 12 years of age, long-term continuous topical corticosteroid therapy should be avoided where possible, as adrenal suppression is more likely to occur.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.